
Symptoms & Diagnosis
Cystitis


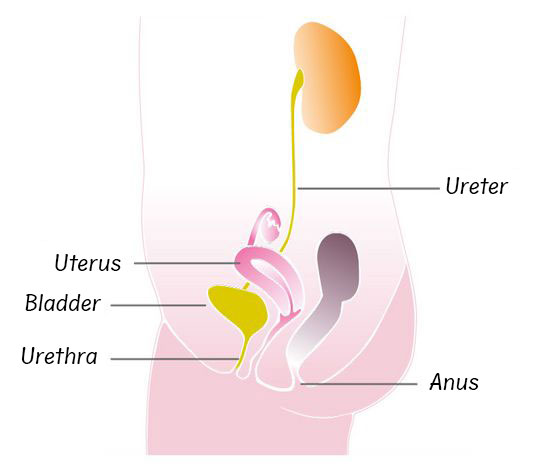
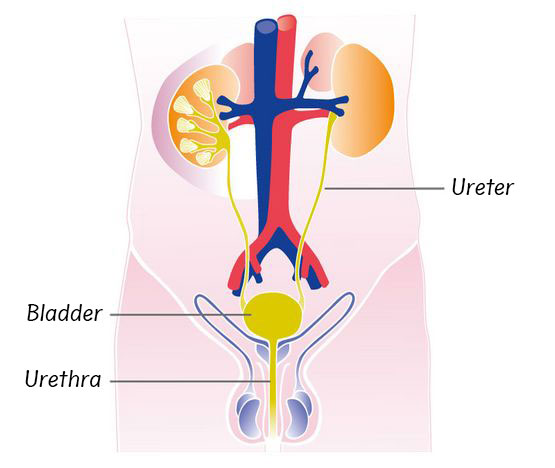
Acute, uncomplicated urinary tract infections are clearly a women's problem1. The reason why women are far more likely to suffer from cystitis than men is because of their anatomy.
Because the female urethra is considerably shorter (4 cm) than in the male (around 20 cm in length), making it easier for bacteria to get into the bladder. In addition, because it is right next to the anus, the urethral opening is easier to reach in women, especially for E. coli bacteria, the main cause of cystitis (inflammation of the bladder)2.
When the bladder catches a chill!
A range of factors contribute to cystitis.
- Cooling in the genital area
- Frequent sexual intercourse
- Changes in female hormone levels during the menopause
- Use of intimate sprays, diaphragms, spermicide gel
The classic symptoms of acute cystitis include:
- severe pain and burning when urinating
- Feeling a constant urge to urinate
- Bladder spasms
The symptoms are very unpleasant and can seriously affect your wellbeing, but they usually respond well to treatment. If treated promptly, the symptoms usually improve quickly
and there are no complications.
Uncomplicated urinary tract infections are rarely accompanied by fever and they never cause pain in your side or back. If such symptoms occur, it suggests that the infection may have spread to the renal pelvis. In such cases, you are strongly advised to see a doctor, as you would if you had blood in your urine.



Preventing and treating acute cystitis
Cystinol offers you tips and hacks on the subjects of acute cystitis or recurrent urinary tract infections. So urinary tract infections don't have a chance.

